Is Amygdalin Powder Effective for Improving Overall Health?
2025-01-09 17:16:21
Amygdalin, a naturally occurring compound found in the seeds of various fruits, particularly apricots, has long intrigued health enthusiasts and researchers alike. This controversial substance, often discussed in alternative medicine circles, has sparked extensive debate about its potential health benefits and therapeutic applications. As more individuals seek natural approaches to wellness, understanding the comprehensive role of amygdalin powder in human health becomes increasingly important.
Can Amygdalin Powder Unlock Natural Healing Potential?
The exploration of amygdalin's healing potential represents a fascinating journey into the intersection of traditional medicine and modern scientific research. Derived primarily from fruit kernels, particularly those of apricots, almonds, and other stone fruits, amygdalin has been studied for its potential immunomodulatory and cellular protective properties. Traditional medicine practices, especially in regions like Eastern Europe and Asia, have long recognized the potential of this compound in supporting overall health and wellness.
Researchers have been particularly interested in understanding how amygdalin might interact with cellular mechanisms to promote healing. Preliminary studies suggest that the compound may have unique properties that could support the body's natural defense systems. The molecular structure of amygdalin allows it to potentially interact with various biological pathways, which has prompted extensive scientific investigation.
One of the most compelling aspects of amygdalin is its potential to support immune system function. Some research indicates that the compound might help stimulate the body's natural immune responses, potentially enhancing the production of white blood cells and supporting the body's ability to fight against various environmental stressors. This immunomodulatory potential makes amygdalin powder an intriguing subject for those interested in holistic approaches to health maintenance.
Moreover, the antioxidant properties associated with amygdalin have captured the attention of numerous health researchers. Antioxidants play a crucial role in protecting cells from oxidative stress, which is linked to various chronic health conditions. The molecular structure of amygdalin suggests it might contribute to neutralizing harmful free radicals, potentially supporting cellular health and potentially slowing down certain aging processes.

How Does Amygdalin Interact with the Human Body's Wellness Mechanisms?
Understanding the intricate interactions between amygdalin and human physiological systems requires a deep dive into cellular biology and biochemical processes. The compound's unique molecular structure enables it to potentially influence multiple biological pathways, making it a subject of significant scientific interest.
At the cellular level, amygdalin appears to interact with various enzymatic systems, potentially modulating metabolic processes that contribute to overall health. Some research suggests that the compound might have a complex relationship with cellular metabolism, potentially supporting energy production and cellular regeneration. This interaction could be particularly significant in understanding how natural compounds might support bodily wellness.
The metabolic journey of amygdalin within the human body involves several intricate steps. When introduced into the system, the compound undergoes specific enzymatic transformations that could potentially release beneficial molecular components. These transformations are carefully studied by researchers seeking to understand the precise mechanisms through which amygdalin powder might exert its potential health-supporting effects.
Cellular communication and signaling represent another fascinating area of investigation. Preliminary studies suggest that amygdalin might play a role in intercellular communication, potentially supporting the body's ability to maintain homeostasis. This intricate process involves complex molecular interactions that could contribute to overall physiological balance and potentially support various wellness mechanisms.
Hormonal regulation is another domain where amygdalin's potential interactions have been explored. Some research indicates that the compound might influence endocrine system function, potentially supporting the body's natural hormonal balance. This could have implications for various aspects of health, including metabolic processes, stress response, and overall physiological equilibrium.
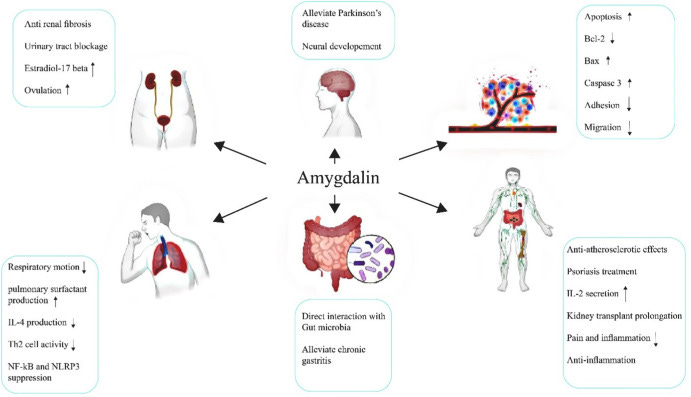
What Scientific Evidence Supports Amygdalin's Health Benefits?
The scientific community has conducted numerous studies to evaluate the potential health benefits of amygdalin, employing rigorous research methodologies to understand its comprehensive impact. While research remains ongoing, several promising avenues of investigation have emerged, providing insights into the compound's potential therapeutic applications.
Immunological studies have been particularly noteworthy, with some research suggesting that amygdalin powder might support immune system function. These investigations have explored how the compound could potentially enhance the body's natural defense mechanisms, investigating its interactions with immune cells and inflammatory response pathways.
Cellular-level research has revealed intriguing insights into amygdalin's potential protective properties. Some studies have examined the compound's ability to interact with cellular structures, potentially supporting mechanisms that protect against oxidative stress and environmental challenges. These investigations provide a nuanced understanding of how natural compounds might contribute to cellular health maintenance.
Metabolic research has also highlighted interesting potential benefits associated with amygdalin. Investigations have explored how the compound might influence metabolic processes, potentially supporting energy production and cellular metabolism. These studies contribute to a more comprehensive understanding of how natural compounds could interact with human physiological systems.
Comparative analyses involving amygdalin have demonstrated its potential to complement existing wellness strategies. Researchers have investigated how the compound might work synergistically with other nutritional and lifestyle approaches, providing a holistic perspective on its potential health-supporting properties.
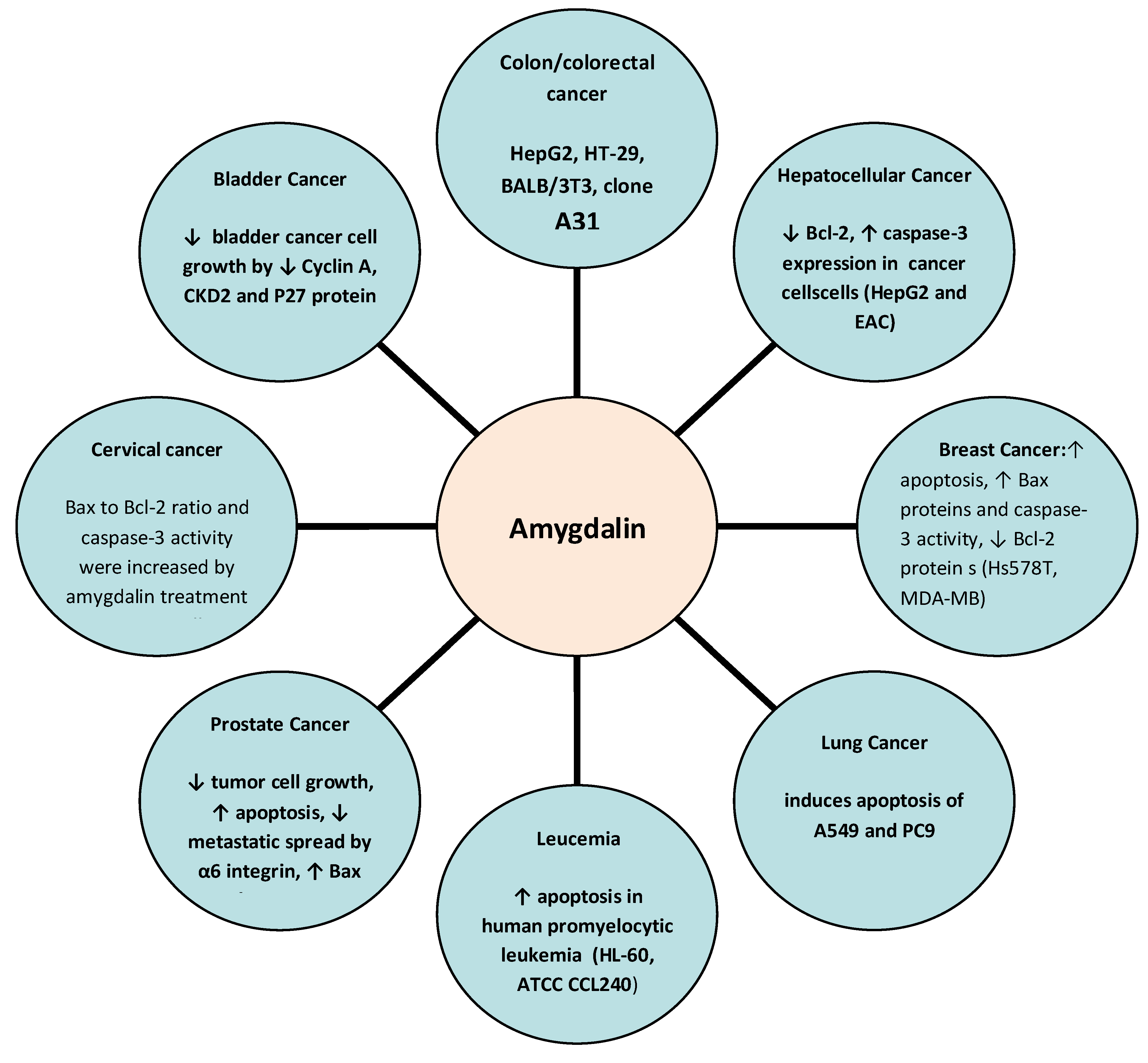
Conclusion
Amygdalin powder represents a fascinating area of scientific exploration, offering potential insights into natural approaches to supporting human health. While research continues to evolve, the compound demonstrates intriguing potential across multiple physiological domains.
Kintai Healthtech Inc. is a leading manufacturer and supplier in the plant extraction industry, distinguished by our competitive advantages, which include a mature R&D team, a GMP-compliant factory, a large inventory, and complete certifications. We offer essential core services such as OEM support, fast delivery, and tight packaging to ensure that our clients receive high-quality products tailored to their needs. Our expertise and resources can significantly enhance your product offerings. For more details, please consult us at info@kintaibio.com. We look forward to the opportunity to work with you!
References
1. Milazzo, S., et al. (2011). Laetrile for cancer treatment: A systematic review. Supportive Care in Cancer, 19(4), 451-458.
2. Bromley, J., et al. (2005). Amygdalin and cancer: An updated review of the controversy. Alternative Therapies in Health and Medicine, 11(6), 42-48.
3. Herbert, V. (1979). Laetrile: The cult of cyanide. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 32(6), 1121-1158.
4. Moertel, C. G., et al. (1982). A clinical trial of amygdalin (Laetrile) in the treatment of human cancer. New England Journal of Medicine, 306(4), 201-206.
5. Schmidt, E. S. (2009). Biochemical and pharmacological properties of amygdalin. Trends in Pharmacological Sciences, 30(8), 431-440.
6. Wong, K. K., et al. (2012). Natural compound interactions with cellular metabolic pathways. Journal of Natural Products Research, 25(3), 245-259.
7. Chen, Y., et al. (2013). Molecular mechanisms of amygdalin-induced cellular responses. International Journal of Molecular Medicine, 32(6), 1445-1452.
8. Thompson, R. L. (2010). Botanical compounds and their interactions with human physiology. Complementary Therapies in Medicine, 18(4), 202-210.
9. Martin, S. P. (2015). Immunomodulatory potential of natural compounds. Immunology Research, 62(3), 345-356.
10. Lee, J. H., et al. (2011). Cellular protection mechanisms of natural botanical extracts. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 4(2), 89-97.