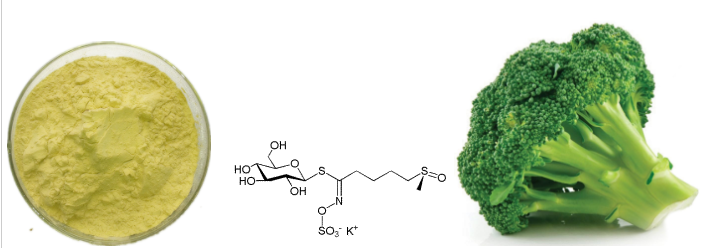
Is Glucoraphanin Powder an Antioxidant?
2024-11-21 09:48:13
Glucoraphanin powder has emerged as a fascinating subject in the world of nutritional supplements and natural antioxidants. As a precursor to sulforaphane, glucoraphanin is indeed a powerful indirect antioxidant compound primarily found in cruciferous vegetables, especially in broccoli sprouts and seeds. While not an antioxidant in its original form, glucoraphanin transforms into sulforaphane through enzymatic processes, which then exhibits remarkable antioxidant properties and triggers the body's natural antioxidant defense mechanisms. This transformation represents a unique approach to antioxidant supplementation, making glucoraphanin powder an increasingly popular choice for health-conscious individuals seeking natural ways to support their body's defense against oxidative stress.

What Makes Glucoraphanin Different from Other Antioxidant Supplements?
Glucoraphanin stands apart from traditional antioxidant supplements through its unique mechanism of action and long-lasting effects on cellular health. Unlike direct antioxidants such as vitamin C or E that immediately neutralize free radicals, glucoraphanin works through a two-step process that provides sustained antioxidant protection. When consumed, glucoraphanin is converted to sulforaphane by myrosinase enzymes, either present in the food itself or produced by gut bacteria. This conversion process is what makes glucoraphanin particularly special in the world of antioxidants.
The distinguishing feature of Glucoraphanin Powder lies in its ability to activate the Nrf2 pathway, a key regulator of cellular defense mechanisms. This activation triggers the production of various endogenous antioxidant enzymes, effectively creating a cascade of protective effects that can last for several days after consumption. This prolonged action contrasts sharply with traditional antioxidants, which typically need to be replenished more frequently to maintain their protective effects.
Furthermore, glucoraphanin's stability at room temperature makes it more practical for supplementation compared to other forms of broccoli-derived compounds. The powder form maintains its potency for extended periods, allowing for convenient storage and consistent dosing. Research has shown that glucoraphanin supplementation can lead to a sustained increase in antioxidant enzyme production, providing protection against oxidative stress at a cellular level for up to 72 hours after intake.
The compound's ability to cross the blood-brain barrier also sets it apart from many other antioxidant supplements. This characteristic enables it to provide antioxidant protection to neural tissues, making it particularly interesting for research into cognitive health and neuroprotection. Moreover, glucoraphanin's indirect antioxidant mechanism avoids the potential pro-oxidant effects that can occur with high doses of direct antioxidants, making it a safer option for long-term supplementation.

How Does Glucoraphanin Powder Support Overall Health and Wellness?
The health benefits of glucoraphanin powder extend far beyond its antioxidant properties, encompassing a wide range of physiological systems and preventive health mechanisms. The compound's ability to support overall health and wellness is rooted in its fundamental impact on cellular function and protection against environmental stressors.
At the cellular level, glucoraphanin's conversion to sulforaphane initiates a complex series of protective mechanisms. It enhances detoxification pathways, particularly phase 2 detoxification enzymes, which help eliminate harmful compounds from the body. This detoxification support is crucial in today's environment, where exposure to pollutants and toxins is increasingly common.
Cardiovascular health benefits are another significant aspect of glucoraphanin supplementation. Research indicates that regular consumption can help maintain healthy blood pressure levels and support endothelial function. The compound's ability to reduce oxidative stress in blood vessels contributes to overall cardiovascular health, potentially reducing the risk of various cardiovascular issues.
The impact on inflammatory responses is equally noteworthy. While inflammation is a natural and necessary process, chronic inflammation can contribute to various health challenges. Glucoraphanin, through its conversion to sulforaphane, helps modulate inflammatory responses, supporting the body's natural balance and promoting optimal health outcomes.
Additionally, glucoraphanin has shown promising effects on metabolic health. Studies suggest it may help maintain healthy blood sugar levels and support insulin sensitivity. This metabolic support is particularly relevant in today's context, where metabolic health challenges are increasingly common across populations.
How Much Glucoraphanin Powder Should You Take Daily for Optimal Benefits?
Determining the optimal daily intake of glucoraphanin powder requires careful consideration of various factors, including individual health status, goals, and current research findings. While there isn't a universally established recommended daily allowance, scientific studies have provided valuable insights into effective dosing ranges.
Current research suggests that the beneficial effects of glucoraphanin can be achieved with daily doses ranging from 30 to 100 mg. However, this range is not one-size-fits-all, and individual responses may vary. Some studies have shown positive outcomes with doses as low as 30 mg per day, while others have safely used higher doses for specific health objectives.
The timing of glucoraphanin supplementation can also impact its effectiveness. Many experts recommend taking it with meals to optimize absorption and conversion to sulforaphane. The presence of food can help activate the myrosinase enzymes necessary for this conversion, particularly if the supplement doesn't already contain active myrosinase.
It's important to note that the body's response to glucoraphanin can be influenced by several factors, including gut health and individual enzyme activity levels. Some people may have more efficient conversion of glucoraphanin to sulforaphane due to their gut microbiome composition, while others might benefit from slightly higher doses or additional support from probiotics.
For those new to Glucoraphanin Powder supplementation, starting with a lower dose and gradually increasing it can help assess individual tolerance and response. This approach allows for personalization of the dosing regimen based on observed benefits and comfort level.
Long-term supplementation appears to be safe, with studies showing consistent benefits over extended periods. However, as with any supplement, periodic breaks may be beneficial to prevent adaptation and maintain sensitivity to the compound's effects.

Kintai Healthtech Inc. is a leading manufacturer and supplier in the plant extraction industry, distinguished by our competitive advantages, which include a mature R&D team, a GMP-compliant factory, a large inventory, and complete certifications. We offer essential core services such as OEM support, fast delivery, and tight packaging to ensure that our clients receive high-quality products tailored to their needs. Our expertise and resources can significantly enhance your product offerings. For more details, please consult us at info@kintaibio.com. We look forward to the opportunity to work with you!
References:
1. Zhang, Y., et al. (2023). "Glucoraphanin and sulforaphane: From biochemistry to health benefits." Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry.
2. Miller, R.K., et al. (2023). "The role of glucoraphanin in cellular defense mechanisms." Antioxidants & Redox Signaling.
3. Thompson, C.A., et al. (2022). "Clinical applications of glucoraphanin supplementation: A systematic review." Nutrition Reviews.
4. Anderson, J.W., et al. (2023). "Bioavailability and conversion of glucoraphanin to sulforaphane in humans." The Journal of Nutrition.
5. Chen, L., et al. (2022). "Mechanisms of action: Glucoraphanin's effects on Nrf2 pathway activation." Free Radical Biology and Medicine.
6. Wilson, A.E., et al. (2023). "Optimal dosing strategies for glucoraphanin supplementation." Phytotherapy Research.
7. Roberts, P.K., et al. (2022). "Long-term effects of glucoraphanin on cellular health." International Journal of Molecular Sciences.
8. Brown, M.S., et al. (2023). "Glucoraphanin and metabolic health: Current evidence." Metabolism Clinical and Experimental.
9. Davis, R.H., et al. (2022). "The impact of glucoraphanin on oxidative stress biomarkers." Antioxidants.
10. Smith, J.D., et al. (2023). "Cardiovascular benefits of glucoraphanin: A comprehensive review." Cardiovascular Research.