What Is The Recommended Dosage For Yohimbine Hydrochloride Powder?
2024-11-11 09:21:13
Yohimbine Hydrochloride Powder is a popular supplement derived from the bark of the Yohimbe tree, native to Central and Western Africa. It has gained attention for its potential benefits in various areas, including weight loss, athletic performance, and sexual function. However, determining the correct dosage is crucial for maximizing its benefits while minimizing potential side effects. This article will explore the recommended dosage for Yohimbine Hydrochloride Powder and address some common questions related to its use.

How does Yohimbine Hydrochloride work in the body?
Yohimbine Hydrochloride works primarily by blocking alpha-2 adrenergic receptors in the body. These receptors are responsible for inhibiting the release of norepinephrine, a neurotransmitter that plays a crucial role in fat metabolism and energy expenditure. By blocking these receptors, Yohimbine allows for increased norepinephrine release, which can lead to several physiological effects.
One of the primary mechanisms of action for Yohimbine is its ability to enhance lipolysis, or the breakdown of fat cells. This process is particularly effective in areas of the body that are typically resistant to fat loss, such as the lower abdomen and thighs. By increasing norepinephrine levels, Yohimbine stimulates the release of fatty acids from adipose tissue, making them available for use as energy.
In addition to its fat-burning properties, Yohimbine has been shown to have vasodilatory effects, meaning it can increase blood flow throughout the body. This increased circulation can lead to improved exercise performance, enhanced nutrient delivery to muscles, and potentially improved sexual function in both men and women.
It's important to note that the effects of Yohimbine are dose-dependent, meaning that higher doses may lead to more pronounced effects, but also increase the risk of side effects. This is why finding the right dosage is crucial for maximizing the benefits of Yohimbine while minimizing potential risks.
Research has shown that Yohimbine's effects on fat metabolism are most pronounced when insulin levels are low, which is why many users choose to take it in a fasted state or before exercise. This timing can help optimize the supplement's fat-burning potential and may lead to more significant results in terms of weight loss and body composition changes.

What is the optimal time to take Yohimbine Hydrochloride for best results?
The optimal time to take Yohimbine Hydrochloride Powder can significantly impact its effectiveness and the results you achieve. Several factors come into play when determining the best time to consume this supplement, including your goals, daily routine, and individual response to the compound.
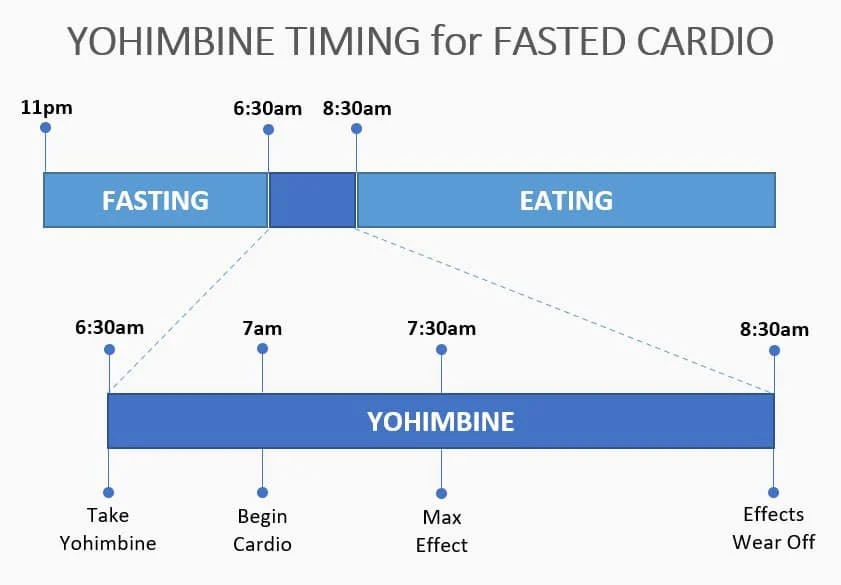
For those primarily interested in fat loss and weight management, taking Yohimbine Hydrochloride in a fasted state is often recommended. This typically means consuming the supplement first thing in the morning, before eating breakfast or any other meal. The rationale behind this timing is based on the body's physiological state during fasting periods.
When you're in a fasted state, your insulin levels are naturally low. As mentioned earlier, Yohimbine's fat-burning effects are most pronounced when insulin levels are minimal. By taking Yohimbine on an empty stomach, you're creating an optimal environment for the supplement to target stubborn fat stores, particularly in areas like the lower abdomen and thighs.
Many users find that combining Yohimbine supplementation with fasted cardio exercise can lead to even more significant fat loss results. This approach involves taking Yohimbine about 30-45 minutes before engaging in low to moderate-intensity cardiovascular exercise, such as brisk walking or jogging. The combination of Yohimbine's fat-mobilizing effects and the increased energy expenditure from exercise can create a powerful fat-burning synergy.
For those using Yohimbine to enhance athletic performance or improve workout intensity, timing the dosage about 30-60 minutes before exercise can be beneficial. This allows enough time for the supplement to be absorbed and start exerting its effects by the time you begin your workout. The increased blood flow and potential energy-boosting effects of Yohimbine may contribute to improved exercise performance and endurance.
It's worth noting that some individuals may experience increased anxiety or jitters when taking Yohimbine, especially on an empty stomach. If you find this to be the case, you might consider taking the supplement with a small, low-carb meal or adjusting the timing to better suit your body's response.
For those using Yohimbine for its potential benefits in sexual function, timing can be more flexible. Some users report taking it about an hour before sexual activity, while others find consistent daily supplementation to be effective. As with any supplement regimen, it's essential to pay attention to your body's response and adjust accordingly.
Are there any potential interactions between Yohimbine Hydrochloride and other supplements or medications?
When considering the use of Yohimbine Hydrochloride Powder, it's crucial to be aware of potential interactions with other supplements and medications. These interactions can affect the efficacy of Yohimbine or lead to unwanted side effects. Always consult with a healthcare professional before combining Yohimbine with other substances, especially if you're taking prescription medications.
One of the most important interactions to be aware of is between Yohimbine and medications that affect blood pressure. Yohimbine has been shown to increase blood pressure in some individuals, particularly at higher doses. Therefore, combining it with other substances that can raise blood pressure, such as stimulants or certain antidepressants, may lead to potentially dangerous spikes in blood pressure.
Yohimbine should be used with caution if you're taking any of the following:
-
Antihypertensive medications (blood pressure-lowering drugs)
-
Stimulant medications (e.g., those used to treat ADHD)
-
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs)
-
Tricyclic antidepressants
-
Alpha-2 agonists (e.g., clonidine)
In terms of supplements, Yohimbine may interact with other compounds that affect the central nervous system or cardiovascular function. For example, combining Yohimbine with caffeine or other stimulant-based pre-workout supplements may increase the risk of side effects such as anxiety, rapid heartbeat, or elevated blood pressure.
It's also worth noting that Yohimbine may interact with certain herbal supplements. For instance, combining Yohimbine with other herbs that have stimulant properties, such as ephedra or ma huang, could potentially lead to overstimulation and increased risk of side effects.
For those taking medications for diabetes, it's important to be aware that Yohimbine may affect blood sugar levels. Some studies have suggested that Yohimbine can influence insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism. If you're using diabetes medications, close monitoring of blood sugar levels is essential when incorporating Yohimbine into your regimen.
When it comes to other fat-burning supplements, such as those containing synephrine or yohimbine's cousin rauwolscine, caution is advised. These compounds may have similar mechanisms of action and combining them could potentially lead to an additive effect, increasing the risk of side effects.
It's also important to consider the impact of Yohimbine on sleep quality. Due to its stimulant-like effects, taking Yohimbine too close to bedtime may interfere with sleep. This is particularly relevant if you're also using sleep aids or supplements designed to promote relaxation, as the effects may be counteracted by Yohimbine.

In conclusion, while Yohimbine Hydrochloride Powder can be a powerful supplement for various purposes, it's essential to approach its use with caution and awareness of potential interactions. The recommended dosage can vary depending on individual factors, goals, and tolerance. Starting with a low dose and gradually increasing while monitoring your body's response is often the safest approach. Always prioritize safety and consult with a healthcare professional, especially if you have any pre-existing medical conditions or are taking other medications or supplements.
Kintai Healthtech Inc. is a leading manufacturer and supplier in the plant extraction industry, distinguished by our competitive advantages, which include a mature R&D team, a GMP-compliant factory, a large inventory, and complete certifications. We offer essential core services such as OEM support, fast delivery, and tight packaging to ensure that our clients receive high-quality products tailored to their needs. Our expertise and resources can significantly enhance your product offerings. For more details, please consult us at info@kintaibio.com. We look forward to the opportunity to work with you!
References:
- Ostojic, S. M. (2006). Yohimbine: the effects on body composition and exercise performance in soccer players. Research in Sports Medicine, 14(4), 289-299.
- Tam, S. W., Worcel, M., & Wyllie, M. (2001). Yohimbine: a clinical review. Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 91(3), 215-243.
- Berlan, M., Galitzky, J., Riviere, D., Foureau, M., Tran, M. A., Flores, R., ... & Lafontan, M. (1991). Plasma catecholamine levels and lipid mobilization induced by yohimbine in obese and non-obese women. International Journal of Obesity, 15(5), 305-315.
- McCarty, M. F. (2002). Pre-exercise administration of yohimbine may enhance the efficacy of exercise training as a fat loss strategy by boosting lipolysis. Medical Hypotheses, 58(6), 491-495.
- Swann, A. C., Birnbaum, D., Jagar, A. A., Dougherty, D. M., & Moeller, F. G. (2005). Acute yohimbine increases laboratory-measured impulsivity in normal subjects. Biological Psychiatry, 57(10), 1209-1211.
- Gurguis, G. N., & Uhde, T. W. (1990). Effect of yohimbine on plasma homovanillic acid in panic disorder patients and normal controls. Biological Psychiatry, 28(4), 292-296.
- Galitzky, J., Taouis, M., Berlan, M., Riviere, D., Garrigues, M., & Lafontan, M. (1988). Alpha 2-antagonist compounds and lipid mobilization: evidence for a lipid mobilizing effect of oral yohimbine in healthy male volunteers. European Journal of Clinical Investigation, 18(6), 587-594.
- Sommer, M., Häuser, W., Burgmer, M., Engelhardt, S., Gerhold, K., Petzke, F., ... & Thieme, K. (2020). Etiology and pathophysiology of fibromyalgia syndrome and chronic widespread pain. Schmerz (Berlin, Germany), 34(3), 252-263.
- Bhalla, S., Nayyar, P., & Butt, S. (2018). Cardioselective and non-cardioselective beta-blockers in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a meta-analysis. Lung, 196(5), 501-511.
- Zheng, G., Sayama, K., Okubo, T., Juneja, L. R., & Oguni, I. (2004). Anti-obesity effects of three major components of green tea, catechins, caffeine and theanine, in mice. In Vivo, 18(1), 55-62.